Auramine – o dye
WHAT IS DYES ?
Definition : generally dye is a colored organic compound or mixture which used for imparting color to the substrate or objects like paper, plastic , cloths , and leather etc.
The long time stability is required for good quality of dye.
The dyed substrate should be resistant to a normal cleaning procedures and stable to light.
Auramine - o is a diarylmethane dye.
It is synthesized from michler's ketone and also from pp’-tetramethyl diamine diphenyl methane.
Chemical properties :
IUPAC NAME : bis [4-(dimethyl amine ) phenyl ] – methanimium chloride.
CAS NUMBER : 2465-27-2 .
STRUCTURE FORMULA :
Molecular formula : C17H22N3Cl .
Molecular weight : 303.83 gm/mole.
Malting point : 267 oC .
Boiling point : 330.5 0C .
Solubility : very soluble in water solubility is (10 gm/liter ) .
Also
soluble in alcohol (ethanol) (20 gm/ liter) .
Color : yellow colored dye.
State : crystalline powder.
Odor : not specific odor or odorless.
Synthesis of auramine-o
Here we have a two different
method for prepare auramine-o.
Method-1 : synthesis of auramine-o from michler’s ketone.
Statement : the reaction of michler’s ketone with NH4Cl , and ZnCl2 , at 150-160 oC, further the auramine base is obtained. Then it is treated with hcl (acidification ) it converted into auramine-o.
Chemical reaction :
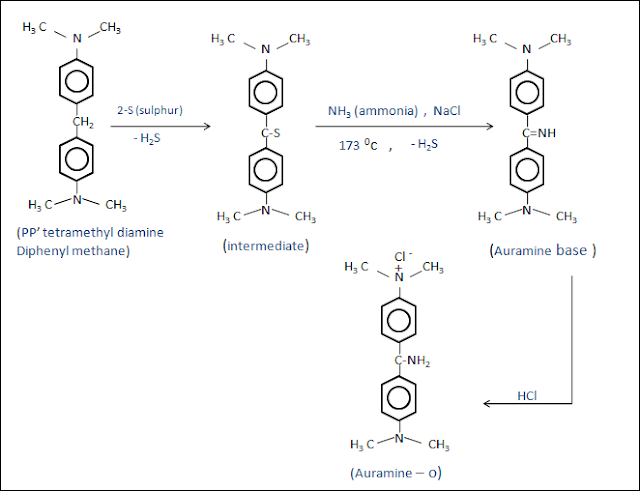
Method – 2 : synthesis of auramine-o from pp’-tetramethyl diamine diphenyl methane.
Statement : pp’-tetramethyl diamine diphenyl methane take as a starting material, the reaction of pp’-tetramethyl diamine diphenyl methane with sulphur forms intermediate , then the reaction of that particular intermediate with ammonia (NH3) and NaCl at 175 oc , gives auramine base , after that the acidification (HCl ) of auramine base yields final product auramine-o .
Chemical reaction :
Uses of auramine-o
Auramine-o dye is widely used for dying many numbers of substrate given below.
(i)
Paper.
(ii)
Silk.
(iii)
Wool.
(iv)
Leather.
(v)
Cotton.
(vi)
Jute.
(vii)
Also used for stain.
(viii)
It is also used as a antiseptic agent.
(ix)
The yellow color of auramine-o is not fast and destroyed by
light , hot water , alkali , oxygen , but still it is used as a dye widely due
to cheaper.
General information
What is staining ? or
staining process
Staining : staining is the process in which substrate colored by using
particular color or dye for the purpose of study basic properties of living or
non-living (dead cells ) biological systems(cells , tissue , cell organelles )
.
For better study of internal structure of biological cells or
tissue staining is applied.
Generally there are two
types of staining here,
(1) Simple staining
In the simple
staining there is a one or single dye is applied to the substrate(living
system).
(2) Differential staining
In the differential
staining there is a more than one dye is applied to the substrate(living system
).
Based on apply staining is
classified as follows
(1) In-vivo or vital
staining
The staining of
living biological system is called in-vivo staining.
It is not harmful for
living systems that is way it is also called vital staining.
(2) In-vitro or non-vital
staining
The staining of
non-living or dead biological systems( dead cells ) is called in-vitro
staining.
It is harmful for
living system that is way it is also called non-vital staining.
Based on chemical nature
staining is divided into three types
(1) Acidic stain
Acidic stain is used
for positively charged substrate or component.
Eg. Malachite green.
(2) Basic stain
Basic stain is used
for negatively charged component (bacteria ).
Eg. Safranin.
(3) Neutral stain
If anion and cataion
both are stained is called neutral stain.
Eg. Wright’s stain.
[અસ્તુ :]





![auramine-o dye or basic yellow-2 dye or diarylmethane dye or bis [4-(dimethyl amine ) phenyl ] – methanimium chloride. -synthesis - study everything](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiUuUnnqOn6NnVrilGzE4o8flSLV681i_5-_72hcw9qHsj9ywHb2JdaJmNpo_rfJwH7V-QYSbI9rSvNqX-GqY41rD0bG7bbjRGramR3ffSIbZWp1pggwr-P-KTY91ZDh3i79x8wS9tsckUQ/w100/structure+formula.PNG)


![ATENOLOL [TENORMIN] - medicinal drug -study everything.](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgGTsBGKNaP_tE51nfYj2h3fKdZpO02gO5BeGfItb45xXsb4Gs_pu7ojGb8kc5WTo3e8qZHTxUwGLRwVrpBxzY-Bld1uR2rsmHRYEj3fX0uV4dEYiMa_46l17eSkXpgPnWb3pgGvDGvkqBU/w100/structural+formula+atenolol.PNG)

1 Comments
Very good
ReplyDeleteplease do not enter any spam link in the comment box.